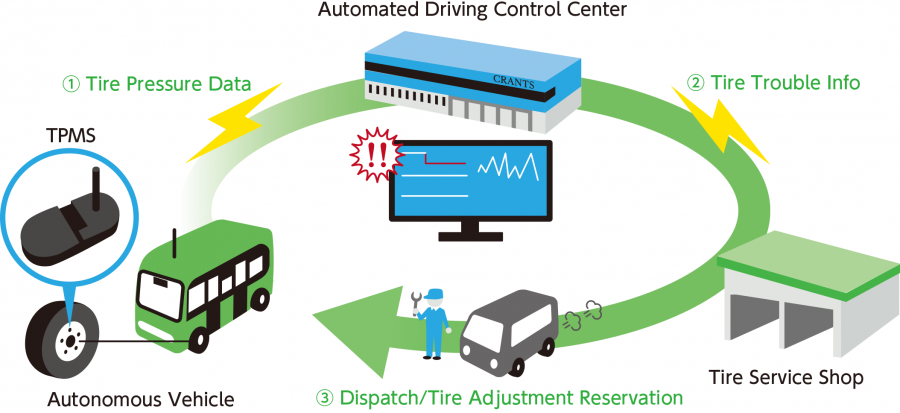
The next crucial step as part of ongoing research between Sumitomo Rubber Industries (SRI) and Gunma University has been made. The collaboration, conducted at the Centre for Research on Adoption of Nextgen Transportation Systems (CRANTS) has completed the process of establishing remote communication between tyre pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) on an autonomous vehicle and a fixed location.
The communication link developed by CRANTS and NTT Data found that real-time tyre data could be sent from the unoccupied vehicle to the Autonomous Driving Control Centre at the testing facility. This breakthrough opens the door for various applications such as predictive maintenance to prevent flat tyres and slow leaks that could be missed without a driver at the wheel.
Commercial applications of this new development allows the control centre to recognise a drop-in tyre pressure and immediately communicate this information to a designated tyre dealer, providing tyre preference and location information.
The research between SRI and CRANTS will continue to work on establishing systems and services that anticipate and pre-empt vehicle safety risks caused by issues with decreasing (or increasing) tyre pressures.
Overview of the Communication Process
・An indirect TPMS mounted inside of the wheel transmits pressure data to the onboard computer system of an autonomous vehicle via BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy).
・The onboard computer system then transmits this data to the CRANTS Control Centre via Connected Technology.
・During automated driving, pressure data from each individual tyre can be monitored from the Control Centre by viewing the Data Management Display.